
Group decision support systems (GDSS) and the more generally described computer-supported collaborative work systems (CSCWS) aid group-level decision making of a semistructured or unstructured variety.

On the strategic level of management we find executive support systems (ESS).
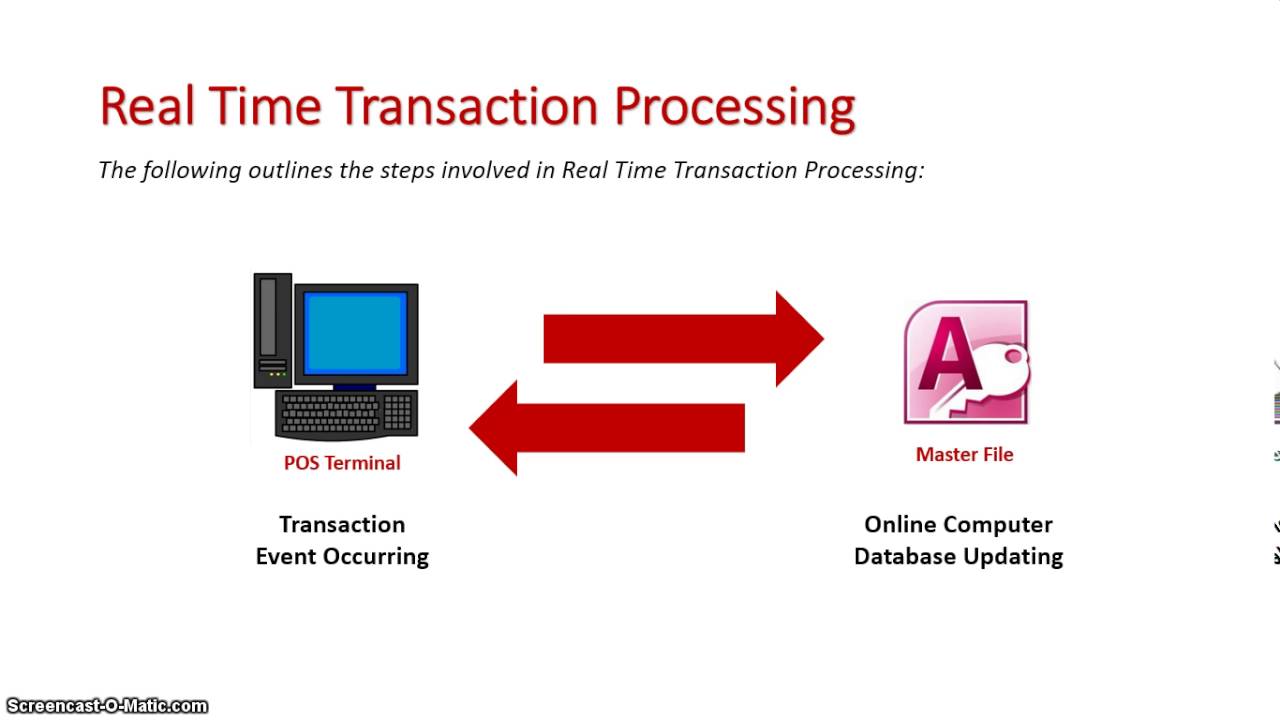
Expert systems apply the expertise of decision makers to solve specific, structured problems. Higher-level systems include management information systems (MIS) and decision support systems (DSS). Transaction processing systems (TPS) function at the operational level of the organization office automation systems (OAS) and knowledge work systems (KWS) support work at the knowledge level. Can you imagine trying to run a business without transaction processing systems and databases to keep track of the information about the day-to-day operations? Databases and information systems are the lifeblood of virtually every business, large or small.Information systems are developed for different purposes, depending on the needs of human users and the business. Results are often aggregations.Īlthough some businesses, especially small businesses, may not utilize Decision Support Systems, all businesses require Transaction Processing Systems and some level of Management Information Systems. Standard SQL with small datasets returnedĬomplex queries and combinations of data. Not normalized other designs such as star or snowflake To support strategic planning and decision makingĬonsolidation of internal operational data and externally acquired data Table 1.2 summarizes some of the differences between these two types of databases. In other words, an OLAP database is designed to support data analysis. In this situation, it is unnecessary to rapidly extract individual customer information or even identify individual customer purchases. For example, a data analysis that looks at trends in purchases of different types of automobiles from year-to-year and then correlates that information with stock prices or interest rates would require a very different type of database structure. Databases that are organized to optimize data analysis are called Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) databases. DSS require a different type of database structure and organization. On the other hand, DSS usually require in-depth analyses, such as trend analyses or correlation analyses between different items. OLTP databases are designed and built to be fast and efficient in supporting active business processes. This type of database structure, OLTP, is very useful for TPS and MIS, which need to summarize daily transactions.
#EXAMPLES OF TPS TRANSACTION PROCESSING SYSTEM UPDATE#
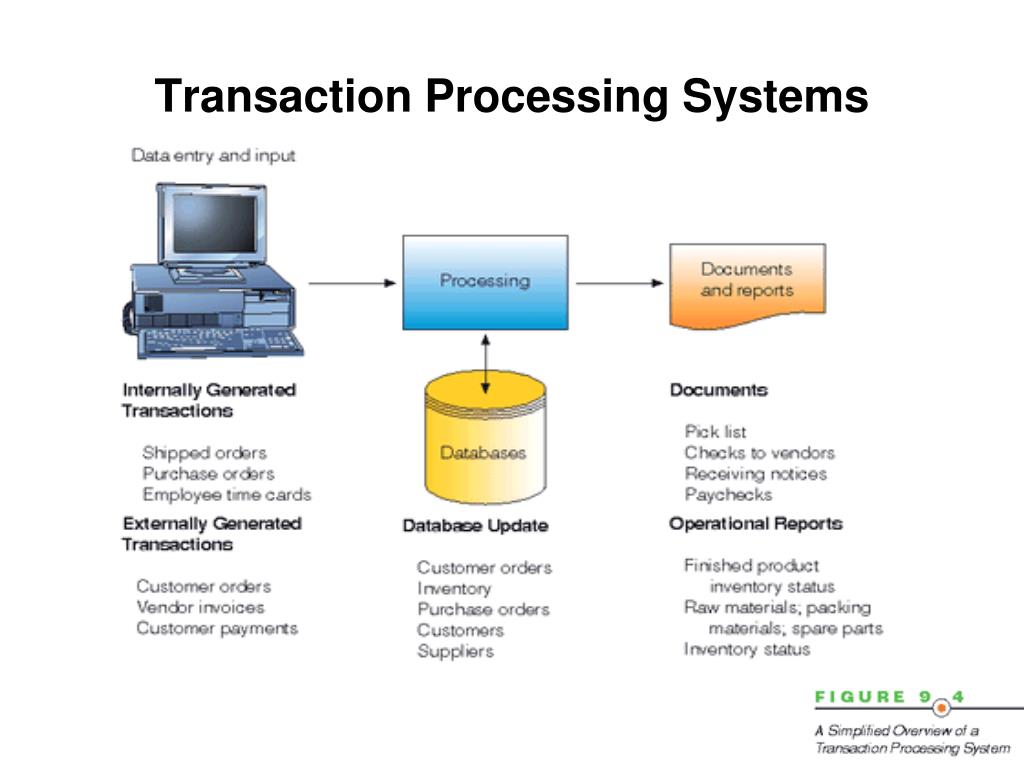
For example, an OLTP database can rapidly display account information about a particular customer and quickly update that customer's account with immediate sales transactions. OLTP types of databases are designed and optimized to allow quick reading of the data and quick updates of individual pieces of data. If the data is organized in a manner that facilitates the rapid processing of business transactions, it is called an Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) database. It is also possible to consider only the method used to organize the data in the database apart from the front end application. In the above table, the three basic types of information systems include all three components-front end, DBMS, and data. In addition, sophisticated modeling and analysis tools are used to extract and manipulate the data.Īs you learned in a previous section about the database approach, an information system consists of the front end application, the DBMS or database engine, and the data itself. Sometimes additional database tables are used to record and provide historical data to forecast future trends.Īre designed to do sophisticated modeling and analysis to help executives make strategic decisions.Ī DSS is heavily dependent on data provided by both internal and external database sources. For example, a point of sale system must present prices item by item and then record the sale of a quantity of that item.Īre normally used by middle management to supervise and verify the efficiency of daily activities.ĭata for MIS is usually extracted from the TPS and summarized into a set of management reports. It must also present detailed information to the user as necessary. The database must capture every transaction. A business will have many TPS systems, including: Are used to support the daily activities of the business.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
